Beta-2 microglobulin
| B2M | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | B2M, entrez:567, IMD43, beta-2-microglobulin, Β2 microglobulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 109700 MGI: 88127 HomoloGene: 2987 GeneCards: B2M | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
β2 microglobulin (B2M) is a component of MHC class I molecules. MHC class I molecules have α1, α2, and α3 proteins which are present on all nucleated cells (excluding red blood cells).[5][6] In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein[7] is encoded by the B2M gene.[6][8]
Structure and function
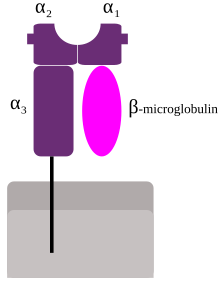
β2 microglobulin lies beside the α3 chain on the cell surface. Unlike α3, β2 has no transmembrane region. Directly above β2 (that is, further away from the cell) lies the α1 chain, which itself is next to the α2.
β2 microglobulin associates not only with the alpha chain of MHC class I molecules, but also with class I-like molecules such as CD1 (5 genes in humans), MR1, the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), and Qa-1 (a form of alloantigen). Nevertheless, the β2 microglobulin gene is outside of the MHC (HLA) locus, on a different chromosome.
An additional function is association with the HFE protein, together regulating the expression of hepcidin in the liver which targets the iron transporter ferroportin on the basolateral membrane of enterocytes and cell membrane of macrophages for degradation resulting in decreased iron uptake from food and decreased iron release from recycled red blood cells in the MPS (mononuclear phagocyte system) respectively. Loss of this function causes iron excess and hemochromatosis.[9]
In a cytomegalovirus infection, a viral protein binds to β2 microglobulin, preventing assembly of MHC class I molecules and their transport to the plasma membrane.
Mice models deficient for the β2 microglobulin gene have been engineered. These mice demonstrate that β2 microglobulin is necessary for cell surface expression of MHC class I and stability of the peptide-binding groove. In fact, in the absence of β2 microglobulin, very limited amounts of MHC class I (classical and non-classical) molecules can be detected on the surface (bare lymphocyte syndrome or BLS). In the absence of MHC class I, CD8+ T cells cannot develop. (CD8+ T cells are a subset of T cells involved in the development of acquired immunity.)[citation needed]
Clinical significance
In patients on long-term hemodialysis, it can aggregate into amyloid fibers that deposit in joint spaces, a disease, known as dialysis-related amyloidosis.
Low levels of β2 microglobulin can indicate non-progression of HIV.[10]
Levels of β2 microglobulin can be elevated in multiple myeloma and lymphoma, though in these cases primary amyloidosis (amyloid light chain) and secondary amyloidosis (amyloid associated protein) are more common.[clarification needed] The normal value of β2 microglobulin is < 2 mg/L.[11] However, with respect to multiple myeloma, the levels of β2 microglobulin may also be at the other end of the spectrum.[12] Diagnostic testing for multiple myeloma includes obtaining the β2 microglobulin level, for this level is an important prognostic indicator. As of 2011[update], a patient with a level < 4 mg/L is expected to have a median survival of 43 months, while one with a level > 4 mg/L has a median survival of only 12 months.[13] β2 microglobulin levels cannot, however, distinguish between monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), which has a better prognosis, and smouldering (low grade) myeloma.[14][15]
Loss-of-function mutations in this gene have been reported in cancer patients unresponsive to immunotherapies.[citation needed]
Virus relevance
β2 microglobulin has been shown to be of high relevance for viral entry of Coxsackievirus A9 and Vaccinia virus (a Poxvirus).[16] For Coxsackievirus A9, it is likely that β2 microglobulin is required for the transport to plasma membrane of the identified receptor, the Human Neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn).[17] However, the specific function for Vaccinia virus has not yet been elucidated.
References
- ^ a b c ENSG00000273686 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000166710, ENSG00000273686 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000060802 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: Beta-2-microglobulin".
- ^ a b Güssow D, Rein R, Ginjaar I, Hochstenbach F, Seemann G, Kottman A, et al. (November 1987). "The human beta 2-microglobulin gene. Primary structure and definition of the transcriptional unit". Journal of Immunology. 139 (9): 3132–8. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.139.9.3132. PMID 3312414. S2CID 38290153.
- ^ Cunningham BA, Wang JL, Berggård I, Peterson PA (November 1973). "The complete amino acid sequence of beta 2-microglobulin". Biochemistry. 12 (24): 4811–22. doi:10.1021/bi00748a001. PMID 4586824.
- ^ Suggs SV, Wallace RB, Hirose T, Kawashima EH, Itakura K (November 1981). "Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 78 (11): 6613–7. Bibcode:1981PNAS...78.6613S. doi:10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. PMC 349099. PMID 6171820.
- ^ Hundall SD (2011). "Chapter 3: Iron, Heme, and Hemoglobin". Hematology: A Pathophysiologic Approach (1st ed.). Elsevier - Health Sciences Division. pp. 17–25. ISBN 978-0-323-04311-3.
- ^ Rao M, Sayal SK, Uppal SS, Gupta RM, Ohri VC, Banerjee S (October 1997). "Beta-2-Microglobulin Levels in Human-Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Subjects". Medical Journal, Armed Forces India. 53 (4): 251–254. doi:10.1016/S0377-1237(17)30746-3. PMC 5531080. PMID 28769505.
- ^ Pignone M, Nicoll D, McPhee SJ (2004). Pocket guide to diagnostic tests (4th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 191. ISBN 0-07-141184-4.
- ^ "Amyloidosis". The Lecturio Medical Concept Library. Retrieved 28 June 2021.
- ^ Munshi NC, Longo DL, Anderson KC (2011). "Chapter 111: Plasma Cell Disorders". In Loscalzo J, Longo DL, Fauci AS, Dennis LK, Hauser SL (eds.). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (18th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 936–44. ISBN 978-0-07-174889-6.
- ^ Rajkumar SV (2005). "MGUS and smoldering multiple myeloma: update on pathogenesis, natural history, and management". Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program. 2005: 340–5. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2005.1.340. PMID 16304401.
- ^ Bataille R, Klein B (November 1992). "Serum levels of beta 2 microglobulin and interleukin-6 to differentiate monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance". Blood. 80 (9): 2433–4. doi:10.1182/blood.V80.9.2433.2433. PMID 1421418.
- ^ Matía A, Lorenzo MM, Romero-Estremera YC, Sánchez-Puig JM, Zaballos A, Blasco R (27 December 2022). "Identification of β2 microglobulin, the product of B2M gene, as a Host Factor for Vaccinia Virus Infection by Genome-Wide CRISPR genetic screens". PLOS Pathogens. 18 (12): e1010800. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1010800. PMC 9829182. PMID 36574441.
- ^ Zhao X, Zhang G, Liu S, Chen X, Peng R, Dai L, et al. (May 2019). "Human Neonatal Fc Receptor Is the Cellular Uncoating Receptor for Enterovirus B". Cell. 177 (6): 1553–1565.e16. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.035. PMC 7111318. PMID 31104841.
Further reading
- Huang WC, Havel JJ, Zhau HE, Qian WP, Lue HW, Chu CY, et al. (September 2008). "Beta2-microglobulin signaling blockade inhibited androgen receptor axis and caused apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells". Clinical Cancer Research. 14 (17): 5341–7. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0793. PMC 3032570. PMID 18765525.
- Huang WC, Wu D, Xie Z, Zhau HE, Nomura T, Zayzafoon M, et al. (September 2006). "beta2-microglobulin is a signaling and growth-promoting factor for human prostate cancer bone metastasis". Cancer Research. 66 (18): 9108–16. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1996. PMID 16982753.
- Winchester JF, Salsberg JA, Levin NW (October 2003). "Beta-2 microglobulin in ESRD: an in-depth review". Advances in Renal Replacement Therapy. 10 (4): 279–309. doi:10.1053/j.arrt.2003.11.003. PMID 14681859.
- Krangel MS, Orr HT, Strominger JL (December 1979). "Assembly and maturation of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo". Cell. 18 (4): 979–91. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(79)90210-1. PMID 93026.
- Okon M, Bray P, Vucelić D (September 1992). "1H NMR assignments and secondary structure of human beta 2-microglobulin in solution". Biochemistry. 31 (37): 8906–15. doi:10.1021/bi00152a030. PMID 1390678.
- Guo HC, Jardetzky TS, Garrett TP, Lane WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (November 1992). "Different length peptides bind to HLA-Aw68 similarly at their ends but bulge out in the middle". Nature. 360 (6402): 364–6. Bibcode:1992Natur.360..364G. doi:10.1038/360364a0. PMID 1448153. S2CID 4324984.
- Gattoni-Celli S, Kirsch K, Timpane R, Isselbacher KJ (March 1992). "Beta 2-microglobulin gene is mutated in a human colon cancer cell line (HCT) deficient in the expression of HLA class I antigens on the cell surface". Cancer Research. 52 (5): 1201–4. PMID 1737380.
- Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Wiley DC (May 1991). "Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 A resolution". Journal of Molecular Biology. 219 (2): 277–319. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(91)90567-P. PMID 2038058.
- Caruana RJ, Lobel SA, Leffell MS, Campbell H, Cheek PL (December 1990). "Tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and beta 2-microglobulin levels in chronic hemodialysis patients". The International Journal of Artificial Organs. 13 (12): 794–8. doi:10.1177/039139889001301205. PMID 2289831. S2CID 24952854.
- Connors LH, Shirahama T, Skinner M, Fenves A, Cohen AS (September 1985). "In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from intact beta 2-microglobulin". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 131 (3): 1063–8. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(85)90198-6. PMID 2413854.
- Hochman JH, Shimizu Y, DeMars R, Edidin M (April 1988). "Specific associations of fluorescent beta-2-microglobulin with cell surfaces. The affinity of different H-2 and HLA antigens for beta-2-microglobulin". Journal of Immunology. 140 (7): 2322–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.140.7.2322. PMID 2450918. S2CID 34035543.
- Homma N, Gejyo F, Isemura M, Arakawa M (1989). "Collagen-binding affinity of beta-2-microglobulin, a preprotein of hemodialysis-associated amyloidosis". Nephron. 53 (1): 37–40. doi:10.1159/000185699. PMID 2674742.
- Bataille R, Grenier J, Commes T (1988). "In vitro production of beta 2 microglobulin by human myeloma cells". Cancer Investigation. 6 (3): 271–7. doi:10.3109/07357908809080649. PMID 3048575.
- Hönig R, Marsen T, Schad S, Barth C, Pollok M, Baldamus CA (November 1988). "Correlation of beta-2-microglobulin concentration changes to changes of distribution volume". The International Journal of Artificial Organs. 11 (6): 459–64. PMID 3060434.
- Bjorkman PJ, Saper MA, Samraoui B, Bennett WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1987). "Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2". Nature. 329 (6139): 506–12. Bibcode:1987Natur.329..506B. doi:10.1038/329506a0. PMID 3309677. S2CID 4373217.
- Güssow D, Rein R, Ginjaar I, Hochstenbach F, Seemann G, Kottman A, et al. (November 1987). "The human beta 2-microglobulin gene. Primary structure and definition of the transcriptional unit". Journal of Immunology. 139 (9): 3132–8. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.139.9.3132. PMID 3312414. S2CID 38290153.
- Cunningham BA, Wang JL, Berggård I, Peterson PA (November 1973). "The complete amino acid sequence of beta 2-microglobulin". Biochemistry. 12 (24): 4811–22. doi:10.1021/bi00748a001. PMID 4586824.
- Suggs SV, Wallace RB, Hirose T, Kawashima EH, Itakura K (November 1981). "Use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes: isolation of cloned cDNA sequences for human beta 2-microglobulin". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 78 (11): 6613–7. Bibcode:1981PNAS...78.6613S. doi:10.1073/pnas.78.11.6613. PMC 349099. PMID 6171820.
- Momoi T, Suzuki M, Titani K, Hisanaga S, Ogawa H, Saito A (May 1995). "Amino acid sequence of a modified beta 2-microglobulin in renal failure patient urine and long-term dialysis patient blood". Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 236 (2): 135–44. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(95)06039-G. PMID 7554280.
- Collins EJ, Garboczi DN, Karpusas MN, Wiley DC (February 1995). "The three-dimensional structure of a class I major histocompatibility complex molecule missing the alpha 3 domain of the heavy chain". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92 (4): 1218–21. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.1218C. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.4.1218. PMC 42670. PMID 7862664.
- Matoba R, Okubo K, Hori N, Fukushima A, Matsubara K (September 1994). "The addition of 5'-coding information to a 3'-directed cDNA library improves analysis of gene expression". Gene. 146 (2): 199–207. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90293-3. PMID 8076819.
- Wang Z, Cao Y, Albino AP, Zeff RA, Houghton A, Ferrone S (February 1993). "Lack of HLA class I antigen expression by melanoma cells SK-MEL-33 caused by a reading frameshift in beta 2-microglobulin messenger RNA". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 91 (2): 684–92. doi:10.1172/JCI116249. PMC 288010. PMID 8432869.
External links
- beta+2-Microglobulin at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human B2M genome location and B2M gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P61769 (Beta-2 microglobulin) at the PDBe-KB.
- v
- t
- e
-
 1a1m: MHC CLASS I MOLECULE B*5301 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE TPYDINQML FROM GAG PROTEIN OF HIV2
1a1m: MHC CLASS I MOLECULE B*5301 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE TPYDINQML FROM GAG PROTEIN OF HIV2 -
 1a1n: MHC CLASS I MOLECULE B*3501 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE VPLRPMTY FROM THE NEF PROTEIN (75-82) OF HIV1
1a1n: MHC CLASS I MOLECULE B*3501 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE VPLRPMTY FROM THE NEF PROTEIN (75-82) OF HIV1 -
 1a1o: MHC CLASS I MOLECULE B*5301 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE LS6 (KPIVQYDNF) FROM THE MALARIA PARASITE P. FALCIPARUM
1a1o: MHC CLASS I MOLECULE B*5301 COMPLEXED WITH PEPTIDE LS6 (KPIVQYDNF) FROM THE MALARIA PARASITE P. FALCIPARUM -
 1a6z: HFE (HUMAN) HEMOCHROMATOSIS PROTEIN
1a6z: HFE (HUMAN) HEMOCHROMATOSIS PROTEIN -
 1a9b: DECAMER-LIKE CONFORMATION OF A NANO-PEPTIDE BOUND TO HLA-B3501 DUE TO NONSTANDARD POSITIONING OF THE C-TERMINUS
1a9b: DECAMER-LIKE CONFORMATION OF A NANO-PEPTIDE BOUND TO HLA-B3501 DUE TO NONSTANDARD POSITIONING OF THE C-TERMINUS -
 1a9e: DECAMER-LIKE CONFORMATION OF A NANO-PEPTIDE BOUND TO HLA-B3501 DUE TO NONSTANDARD POSITIONING OF THE C-TERMINUS
1a9e: DECAMER-LIKE CONFORMATION OF A NANO-PEPTIDE BOUND TO HLA-B3501 DUE TO NONSTANDARD POSITIONING OF THE C-TERMINUS -
 1agb: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGRKKYKL-3R MUTATION)
1agb: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGRKKYKL-3R MUTATION) -
 1agc: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKKYQL-7Q MUTATION)
1agc: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKKYQL-7Q MUTATION) -
 1agd: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKKYKL-INDEX PEPTIDE)
1agd: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKKYKL-INDEX PEPTIDE) -
 1age: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKKYRL-7R MUTATION)
1age: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKKYRL-7R MUTATION) -
 1agf: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKRYKL-5R MUTATION)
1agf: ANTAGONIST HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDES INDUCE STRUCTURAL CHANGES IN HLA B8-HIV-1 GAG PEPTIDE (GGKKRYKL-5R MUTATION) -
 1akj: COMPLEX OF THE HUMAN MHC CLASS I GLYCOPROTEIN HLA-A2 AND THE T CELL CORECEPTOR CD8
1akj: COMPLEX OF THE HUMAN MHC CLASS I GLYCOPROTEIN HLA-A2 AND THE T CELL CORECEPTOR CD8 -
 1ao7: COMPLEX BETWEEN HUMAN T-CELL RECEPTOR, VIRAL PEPTIDE (TAX), AND HLA-A 0201
1ao7: COMPLEX BETWEEN HUMAN T-CELL RECEPTOR, VIRAL PEPTIDE (TAX), AND HLA-A 0201 -
 1b0g: CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN (HLA-A2.1)/BETA 2-MICROGLOBULIN/PEPTIDE P1049 COMPLEX
1b0g: CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN (HLA-A2.1)/BETA 2-MICROGLOBULIN/PEPTIDE P1049 COMPLEX -
 1b0r: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A*0201 COMPLEXED WITH A PEPTIDE WITH THE CARBOXYL-TERMINAL GROUP SUBSTITUTED BY A METHYL GROUP
1b0r: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A*0201 COMPLEXED WITH A PEPTIDE WITH THE CARBOXYL-TERMINAL GROUP SUBSTITUTED BY A METHYL GROUP -
 1bd2: COMPLEX BETWEEN HUMAN T-CELL RECEPTOR B7, VIRAL PEPTIDE (TAX) AND MHC CLASS I MOLECULE HLA-A 0201
1bd2: COMPLEX BETWEEN HUMAN T-CELL RECEPTOR B7, VIRAL PEPTIDE (TAX) AND MHC CLASS I MOLECULE HLA-A 0201 -
 1c16: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE GAMMA/DELTA T CELL LIGAND T22
1c16: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE GAMMA/DELTA T CELL LIGAND T22 -
 1ce6: MHC CLASS I H-2DB COMPLEXED WITH A SENDAI VIRUS NUCLEOPROTEIN PEPTIDE
1ce6: MHC CLASS I H-2DB COMPLEXED WITH A SENDAI VIRUS NUCLEOPROTEIN PEPTIDE -
 1cg9: COMPLEX RECOGNITION OF THE SUPERTYPIC BW6-DETERMINANT ON HLA-B AND-C MOLECULES BY THE MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY SFR8-B6
1cg9: COMPLEX RECOGNITION OF THE SUPERTYPIC BW6-DETERMINANT ON HLA-B AND-C MOLECULES BY THE MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY SFR8-B6 -
 1de4: HEMOCHROMATOSIS PROTEIN HFE COMPLEXED WITH TRANSFERRIN RECEPTOR
1de4: HEMOCHROMATOSIS PROTEIN HFE COMPLEXED WITH TRANSFERRIN RECEPTOR -
 1duy: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A*0201/OCTAMERIC TAX PEPTIDE COMPLEX
1duy: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A*0201/OCTAMERIC TAX PEPTIDE COMPLEX -
 1duz: HUMAN CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN (HLA-A 0201) IN COMPLEX WITH A NONAMERIC PEPTIDE FROM HTLV-1 TAX PROTEIN
1duz: HUMAN CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN (HLA-A 0201) IN COMPLEX WITH A NONAMERIC PEPTIDE FROM HTLV-1 TAX PROTEIN -
 1e27: NONSTANDARD PEPTIDE BINDING OF HLA-B*5101 COMPLEXED WITH HIV IMMUNODOMINANT EPITOPE KM1(LPPVVAKEI)
1e27: NONSTANDARD PEPTIDE BINDING OF HLA-B*5101 COMPLEXED WITH HIV IMMUNODOMINANT EPITOPE KM1(LPPVVAKEI) -
 1e28: NONSTANDARD PEPTIDE BINDING OF HLA-B*5101 COMPLEXED WITH HIV IMMUNODOMINANT EPITOPE KM2(TAFTIPSI)
1e28: NONSTANDARD PEPTIDE BINDING OF HLA-B*5101 COMPLEXED WITH HIV IMMUNODOMINANT EPITOPE KM2(TAFTIPSI) -
 1eey: Crystal Structure Determination Of HLA A2 Complexed to Peptide GP2 with the substitution (I2L/V5L/L9V)
1eey: Crystal Structure Determination Of HLA A2 Complexed to Peptide GP2 with the substitution (I2L/V5L/L9V) -
 1eez: Crystal Structure Determination of HLA-A2.1 Complexed to GP2 Peptide Variant(I2L/V5L)
1eez: Crystal Structure Determination of HLA-A2.1 Complexed to GP2 Peptide Variant(I2L/V5L) -
 1efx: STRUCTURE OF A COMPLEX BETWEEN THE HUMAN NATURAL KILLER CELL RECEPTOR KIR2DL2 AND A CLASS I MHC LIGAND HLA-CW3
1efx: STRUCTURE OF A COMPLEX BETWEEN THE HUMAN NATURAL KILLER CELL RECEPTOR KIR2DL2 AND A CLASS I MHC LIGAND HLA-CW3 -
 1exu: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN MHC-RELATED FC RECEPTOR
1exu: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN MHC-RELATED FC RECEPTOR -
 1gzp: CD1B IN COMPLEX WITH GM2 GANGLIOSIDE
1gzp: CD1B IN COMPLEX WITH GM2 GANGLIOSIDE -
 1gzq: CD1B IN COMPLEX WITH PHOPHATIDYLINOSITOL
1gzq: CD1B IN COMPLEX WITH PHOPHATIDYLINOSITOL -
 1hhg: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2
1hhg: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2 -
 1hhh: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2
1hhh: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2 -
 1hhi: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2
1hhi: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2 -
 1hhj: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2
1hhj: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2 -
 1hhk: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2
1hhk: THE ANTIGENIC IDENTITY OF PEPTIDE(SLASH)MHC COMPLEXES: A COMPARISON OF THE CONFORMATION OF FIVE PEPTIDES PRESENTED BY HLA-A2 -
 1hsa: THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B27 AT 2.1 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION SUGGESTS A GENERAL MECHANISM FOR TIGHT PEPTIDE BINDING TO MHC
1hsa: THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B27 AT 2.1 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION SUGGESTS A GENERAL MECHANISM FOR TIGHT PEPTIDE BINDING TO MHC -
 1hsb: DIFFERENT LENGTH PEPTIDES BIND TO HLA-AW68 SIMILARLY AT THEIR ENDS BUT BULGE OUT IN THE MIDDLE
1hsb: DIFFERENT LENGTH PEPTIDES BIND TO HLA-AW68 SIMILARLY AT THEIR ENDS BUT BULGE OUT IN THE MIDDLE -
 1i1f: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CLASS I MHC (HLA-A2.1) COMPLEXED WITH BETA 2-MICROGLOBULIN AND HIV-RT VARIANT PEPTIDE I1Y
1i1f: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CLASS I MHC (HLA-A2.1) COMPLEXED WITH BETA 2-MICROGLOBULIN AND HIV-RT VARIANT PEPTIDE I1Y -
 1i1y: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CLASS I MHC (HLA-A2.1) COMPLEXED WITH BETA 2-MICROGLOBULIN AND HIV-RT VARIANT PEPTIDE I1Y
1i1y: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CLASS I MHC (HLA-A2.1) COMPLEXED WITH BETA 2-MICROGLOBULIN AND HIV-RT VARIANT PEPTIDE I1Y -
 1i4f: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A*0201/MAGE-A4-PEPTIDE COMPLEX
1i4f: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A*0201/MAGE-A4-PEPTIDE COMPLEX -
 1i7r: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLASS I MHC A2 IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE P1058
1i7r: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLASS I MHC A2 IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE P1058 -
 1i7t: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLASS I MHC A2 IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE P1049-5V
1i7t: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLASS I MHC A2 IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE P1049-5V -
 1i7u: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLASS I MHC A2 IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE P1049-6V
1i7u: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLASS I MHC A2 IN COMPLEX WITH PEPTIDE P1049-6V -
 1im3: Crystal Structure of the human cytomegalovirus protein US2 bound to the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2/tax
1im3: Crystal Structure of the human cytomegalovirus protein US2 bound to the MHC class I molecule HLA-A2/tax -
 1im9: Crystal structure of the human natural killer cell inhibitory receptor KIR2DL1 bound to its MHC ligand HLA-Cw4
1im9: Crystal structure of the human natural killer cell inhibitory receptor KIR2DL1 bound to its MHC ligand HLA-Cw4 -
 1jf1: Crystal structure of HLA-A2*0201 in complex with a decameric altered peptide ligand from the MART-1/Melan-A
1jf1: Crystal structure of HLA-A2*0201 in complex with a decameric altered peptide ligand from the MART-1/Melan-A -
 1jgd: HLA-B*2709 bound to deca-peptide s10R
1jgd: HLA-B*2709 bound to deca-peptide s10R -
 1jge: HLA-B*2705 bound to nona-peptide m9
1jge: HLA-B*2705 bound to nona-peptide m9 -
 1jht: Crystal structure of HLA-A2*0201 in complex with a nonameric altered peptide ligand (ALGIGILTV) from the MART-1/Melan-A.
1jht: Crystal structure of HLA-A2*0201 in complex with a nonameric altered peptide ligand (ALGIGILTV) from the MART-1/Melan-A. -
 1jnj: NMR solution structure of the human beta2-microglobulin
1jnj: NMR solution structure of the human beta2-microglobulin -
 1k5n: HLA-B*2709 BOUND TO NONA-PEPTIDE M9
1k5n: HLA-B*2709 BOUND TO NONA-PEPTIDE M9 -
 1kpr: The human non-classical major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-E
1kpr: The human non-classical major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-E -
 1ktl: The human non-classical major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-E
1ktl: The human non-classical major histocompatibility complex molecule HLA-E -
 1lds: Crystal Structure of monomeric human beta-2-microglobulin
1lds: Crystal Structure of monomeric human beta-2-microglobulin -
 1lp9: Xenoreactive complex AHIII 12.2 TCR bound to p1049/HLA-A2.1
1lp9: Xenoreactive complex AHIII 12.2 TCR bound to p1049/HLA-A2.1 -
 1m05: HLA B8 in complex with an Epstein Barr Virus determinant
1m05: HLA B8 in complex with an Epstein Barr Virus determinant -
 1m6o: Crystal Structure of HLA B*4402 in complex with HLA DPA*0201 peptide
1m6o: Crystal Structure of HLA B*4402 in complex with HLA DPA*0201 peptide -
 1mhe: THE HUMAN NON-CLASSICAL MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX MOLECULE HLA-E
1mhe: THE HUMAN NON-CLASSICAL MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX MOLECULE HLA-E -
 1mi5: The crystal structure of LC13 TcR in complex with HLAB8-EBV peptide complex
1mi5: The crystal structure of LC13 TcR in complex with HLAB8-EBV peptide complex -
 1n2r: A natural selected dimorphism in HLA B*44 alters self, peptide reportoire and T cell recognition.
1n2r: A natural selected dimorphism in HLA B*44 alters self, peptide reportoire and T cell recognition. -
 1of2: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2709 COMPLEXED WITH THE VASOACTIVE INTESTINAL PEPTIDE TYPE 1 RECEPTOR (VIPR) PEPTIDE (RESIDUES 400-408)
1of2: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2709 COMPLEXED WITH THE VASOACTIVE INTESTINAL PEPTIDE TYPE 1 RECEPTOR (VIPR) PEPTIDE (RESIDUES 400-408) -
 1oga: A STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR IMMUNODOMINANT HUMAN T-CELL RECEPTOR RECOGNITION.
1oga: A STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR IMMUNODOMINANT HUMAN T-CELL RECEPTOR RECOGNITION. -
 1ogt: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2705 COMPLEXED WITH THE VASOACTIVE INTESTINAL PEPTIDE TYPE 1 RECEPTOR (VIPR) PEPTIDE (RESIDUES 400-408)
1ogt: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2705 COMPLEXED WITH THE VASOACTIVE INTESTINAL PEPTIDE TYPE 1 RECEPTOR (VIPR) PEPTIDE (RESIDUES 400-408) -
 1onq: Crystal Structure of CD1a in Complex with a Sulfatide
1onq: Crystal Structure of CD1a in Complex with a Sulfatide -
 1p7q: Crystal Structure of HLA-A2 Bound to LIR-1, a Host and Viral MHC Receptor
1p7q: Crystal Structure of HLA-A2 Bound to LIR-1, a Host and Viral MHC Receptor -
 1py4: Beta2 microglobulin mutant H31Y displays hints for amyloid formations
1py4: Beta2 microglobulin mutant H31Y displays hints for amyloid formations -
 1q94: Structures of HLA-A*1101 in complex with immunodominant nonamer and decamer HIV-1 epitopes clearly reveal the presence of a middle anchor residue
1q94: Structures of HLA-A*1101 in complex with immunodominant nonamer and decamer HIV-1 epitopes clearly reveal the presence of a middle anchor residue -
 1qew: HUMAN CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN (HLA-A 0201) COMPLEX WITH A NONAMERIC PEPTIDE FROM MELANOMA-ASSOCIATED ANTIGEN 3 (RESIDUES 271-279)
1qew: HUMAN CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN (HLA-A 0201) COMPLEX WITH A NONAMERIC PEPTIDE FROM MELANOMA-ASSOCIATED ANTIGEN 3 (RESIDUES 271-279) -
 1qlf: MHC CLASS I H-2DB COMPLEXED WITH GLYCOPEPTIDE K3G
1qlf: MHC CLASS I H-2DB COMPLEXED WITH GLYCOPEPTIDE K3G -
 1qqd: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-CW4, A LIGAND FOR THE KIR2D NATURAL KILLER CELL INHIBITORY RECEPTOR
1qqd: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-CW4, A LIGAND FOR THE KIR2D NATURAL KILLER CELL INHIBITORY RECEPTOR -
 1qr1: POOR BINDING OF A HER-2/NEU EPITOPE (GP2) TO HLA-A2.1 IS DUE TO A LACK OF INTERACTIONS IN THE CENTER OF THE PEPTIDE
1qr1: POOR BINDING OF A HER-2/NEU EPITOPE (GP2) TO HLA-A2.1 IS DUE TO A LACK OF INTERACTIONS IN THE CENTER OF THE PEPTIDE -
 1qrn: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN A6 TCR COMPLEXED WITH HLA-A2 BOUND TO ALTERED HTLV-1 TAX PEPTIDE P6A
1qrn: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN A6 TCR COMPLEXED WITH HLA-A2 BOUND TO ALTERED HTLV-1 TAX PEPTIDE P6A -
 1qse: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN A6-TCR BOUND TO HLA-A2 COMPLEXED WITH ALTERED HTLV-1 TAX PEPTIDE V7R
1qse: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN A6-TCR BOUND TO HLA-A2 COMPLEXED WITH ALTERED HTLV-1 TAX PEPTIDE V7R -
 1qsf: STRUCTURE OF A6-TCR BOUND TO HLA-A2 COMPLEXED WITH ALTERED HTLV-1 TAX PEPTIDE Y8A
1qsf: STRUCTURE OF A6-TCR BOUND TO HLA-A2 COMPLEXED WITH ALTERED HTLV-1 TAX PEPTIDE Y8A -
 1qvo: STRUCTURES OF HLA-A*1101 IN COMPLEX WITH IMMUNODOMINANT NONAMER AND DECAMER HIV-1 EPITOPES CLEARLY REVEAL THE PRESENCE OF A MIDDLE ANCHOR RESIDUE
1qvo: STRUCTURES OF HLA-A*1101 IN COMPLEX WITH IMMUNODOMINANT NONAMER AND DECAMER HIV-1 EPITOPES CLEARLY REVEAL THE PRESENCE OF A MIDDLE ANCHOR RESIDUE -
 1r3h: Crystal Structure of T10
1r3h: Crystal Structure of T10 -
 1s8d: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-3A
1s8d: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-3A -
 1s9w: Crystal Structure Analysis of NY-ESO-1 epitope, SLLMWITQC, in complex with HLA-A2
1s9w: Crystal Structure Analysis of NY-ESO-1 epitope, SLLMWITQC, in complex with HLA-A2 -
 1s9x: Crystal Structure Analysis of NY-ESO-1 epitope analogue, SLLMWITQA, in complex with HLA-A2
1s9x: Crystal Structure Analysis of NY-ESO-1 epitope analogue, SLLMWITQA, in complex with HLA-A2 -
 1s9y: Crystal Structure Analysis of NY-ESO-1 epitope analogue, SLLMWITQS, in complex with HLA-A2
1s9y: Crystal Structure Analysis of NY-ESO-1 epitope analogue, SLLMWITQS, in complex with HLA-A2 -
 1sys: Crystal structure of HLA, B*4403, and peptide EEPTVIKKY
1sys: Crystal structure of HLA, B*4403, and peptide EEPTVIKKY -
 1syv: HLA-B*4405 complexed to the dominant self ligand EEFGRAYGF
1syv: HLA-B*4405 complexed to the dominant self ligand EEFGRAYGF -
 1t1w: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-3F6I8V
1t1w: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-3F6I8V -
 1t1x: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-4L
1t1x: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-4L -
 1t1y: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-5V
1t1y: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-5V -
 1t1z: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-6A
1t1z: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-6A -
 1t20: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-6I
1t20: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9-6I -
 1t21: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9, monoclinic crystal
1t21: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9, monoclinic crystal -
 1t22: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9, orthorhombic crystal
1t22: Structural basis for degenerate recognition of HIV peptide variants by cytotoxic lymphocyte, variant SL9, orthorhombic crystal -
 1tmc: THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF A CLASS I MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX MOLECULE MISSING THE ALPHA3 DOMAIN OF THE HEAVY CHAIN
1tmc: THE THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF A CLASS I MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY COMPLEX MOLECULE MISSING THE ALPHA3 DOMAIN OF THE HEAVY CHAIN -
 1tvb: Crystal structure of Melanoma Antigen gp100(209-217) Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2
1tvb: Crystal structure of Melanoma Antigen gp100(209-217) Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 -
 1tvh: Crystal structure of Modified Melanoma Antigen gp100(209-T2M) Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2
1tvh: Crystal structure of Modified Melanoma Antigen gp100(209-T2M) Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 -
 1uqs: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CD1B WITH A BOUND BACTERIAL GLYCOLIPID
1uqs: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CD1B WITH A BOUND BACTERIAL GLYCOLIPID -
 1uxs: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2705 COMPLEXED WITH THE LATENT MEMBRANE PROTEIN 2 PEPTIDE (LMP2)OF EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS
1uxs: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2705 COMPLEXED WITH THE LATENT MEMBRANE PROTEIN 2 PEPTIDE (LMP2)OF EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS -
 1uxw: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2709 COMPLEXED WITH THE LATENT MEMBRANE PROTEIN 2 PEPTIDE (LMP2) OF EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS
1uxw: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2709 COMPLEXED WITH THE LATENT MEMBRANE PROTEIN 2 PEPTIDE (LMP2) OF EPSTEIN-BARR VIRUS -
 1vgk: The crystal structure of class I Major histocompatibility complex, H-2Kd at 2.0 A resolution
1vgk: The crystal structure of class I Major histocompatibility complex, H-2Kd at 2.0 A resolution -
 1w0v: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2705 COMPLEXED WITH THE SELF-PEPTIDE TIS FROM EGF-RESPONSE FACTOR 1
1w0v: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2705 COMPLEXED WITH THE SELF-PEPTIDE TIS FROM EGF-RESPONSE FACTOR 1 -
 1w0w: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2709 COMPLEXED WITH THE SELF-PEPTIDE TIS FROM EGF-RESPONSE FACTOR 1
1w0w: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-B*2709 COMPLEXED WITH THE SELF-PEPTIDE TIS FROM EGF-RESPONSE FACTOR 1 -
 1w72: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A1:MAGE-A1 IN COMPLEX WITH FAB-HYB3
1w72: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HLA-A1:MAGE-A1 IN COMPLEX WITH FAB-HYB3 -
 1x7q: Crystal structure of HLA-A*1101 with sars nucleocapsid peptide
1x7q: Crystal structure of HLA-A*1101 with sars nucleocapsid peptide -
 1xh3: Conformational Restraints and Flexibility of 14-Meric Peptides in Complex with HLA-B*3501
1xh3: Conformational Restraints and Flexibility of 14-Meric Peptides in Complex with HLA-B*3501 -
 1xr8: Crystal Structures of HLA-B*1501 in Complex with Peptides from Human UbcH6 and Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA-3
1xr8: Crystal Structures of HLA-B*1501 in Complex with Peptides from Human UbcH6 and Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA-3 -
 1xr9: Crystal Structures of HLA-B*1501 in Complex with Peptides from Human UbcH6 and Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA-3
1xr9: Crystal Structures of HLA-B*1501 in Complex with Peptides from Human UbcH6 and Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA-3 -
 1xz0: Crystal structure of CD1a in complex with a synthetic mycobactin lipopeptide
1xz0: Crystal structure of CD1a in complex with a synthetic mycobactin lipopeptide -
 1ydp: 1.9A crystal structure of HLA-G
1ydp: 1.9A crystal structure of HLA-G -
 1ypz: Immune receptor
1ypz: Immune receptor -
 1zhk: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3501 presenting 13-mer EBV antigen LPEPLPQGQLTAY
1zhk: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3501 presenting 13-mer EBV antigen LPEPLPQGQLTAY -
 1zhl: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3508 presenting 13-mer EBV antigen LPEPLPQGQLTAY
1zhl: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3508 presenting 13-mer EBV antigen LPEPLPQGQLTAY -
 1zs8: Crystal Structure of the Murine MHC Class Ib Molecule M10.5
1zs8: Crystal Structure of the Murine MHC Class Ib Molecule M10.5 -
 1zsd: Crystal Structure Of HLA-B*3501 Presenting an 11-Mer EBV Antigen EPLPQGQLTAY
1zsd: Crystal Structure Of HLA-B*3501 Presenting an 11-Mer EBV Antigen EPLPQGQLTAY -
 1zt4: The crystal structure of human CD1d with and without alpha-Galactosylceramide
1zt4: The crystal structure of human CD1d with and without alpha-Galactosylceramide -
 1zvs: Crystal structure of the first class MHC mamu and Tat-Tl8 complex
1zvs: Crystal structure of the first class MHC mamu and Tat-Tl8 complex -
 2a83: Crystal structure of hla-b*2705 complexed with the glucagon receptor (gr) peptide (residues 412-420)
2a83: Crystal structure of hla-b*2705 complexed with the glucagon receptor (gr) peptide (residues 412-420) -
 2ak4: Crystal Structure of SB27 TCR in complex with HLA-B*3508-13mer peptide
2ak4: Crystal Structure of SB27 TCR in complex with HLA-B*3508-13mer peptide -
 2av1: Crystal structure of HTLV-1 TAX peptide Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the E63Q and K66A mutations in the heavy chain.
2av1: Crystal structure of HTLV-1 TAX peptide Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the E63Q and K66A mutations in the heavy chain. -
 2av7: Crystal structure of HTLV-1 TAX peptide Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the K66A mutation in the heavy chain.
2av7: Crystal structure of HTLV-1 TAX peptide Bound to Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the K66A mutation in the heavy chain. -
 2axf: The Immunogenicity of a Viral Cytotoxic T Cell Epitope is controlled by its MHC-bound Conformation
2axf: The Immunogenicity of a Viral Cytotoxic T Cell Epitope is controlled by its MHC-bound Conformation -
 2axg: The Immunogenicity of a Viral Cytotoxic T Cell Epitope is controlled by its MHC-bound Conformation
2axg: The Immunogenicity of a Viral Cytotoxic T Cell Epitope is controlled by its MHC-bound Conformation -
 2bck: Crystal Structure of HLA-A*2402 Complexed with a telomerase peptide
2bck: Crystal Structure of HLA-A*2402 Complexed with a telomerase peptide -
 2bnq: STRUCTURAL AND KINETIC BASIS FOR HEIGHTENED IMMUNOGENICITY OF T CELL VACCINES
2bnq: STRUCTURAL AND KINETIC BASIS FOR HEIGHTENED IMMUNOGENICITY OF T CELL VACCINES -
 2bnr: STRUCTURAL AND KINETIC BASIS FOR HEIGHTENED IMMUNOGENICITY OF T CELL VACCINES
2bnr: STRUCTURAL AND KINETIC BASIS FOR HEIGHTENED IMMUNOGENICITY OF T CELL VACCINES -
 2bsr: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AND KIR3DL1 RECOGNITION OF THREE IMMUNODOMINANT VIRAL PEPTIDES COMPLEXED TO HLA-B2705
2bsr: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AND KIR3DL1 RECOGNITION OF THREE IMMUNODOMINANT VIRAL PEPTIDES COMPLEXED TO HLA-B2705 -
 2bss: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AND KIR3DL1 RECOGNITION OF THREE IMMUNODOMINANT VIRAL PEPTIDES COMPLEXED TO HLA-B2705
2bss: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AND KIR3DL1 RECOGNITION OF THREE IMMUNODOMINANT VIRAL PEPTIDES COMPLEXED TO HLA-B2705 -
 2bst: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AND KIR3DL1 RECOGNITION OF THREE IMMUNODOMINANT VIRAL PEPTIDES COMPLEXED TO HLA-B2705
2bst: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES AND KIR3DL1 RECOGNITION OF THREE IMMUNODOMINANT VIRAL PEPTIDES COMPLEXED TO HLA-B2705 -
 2bsu:
2bsu: -
 2bsv:
2bsv: -
 2bvo: STRUCTURES OF THREE HIV-1 HLA-B5703-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES AND IDENTIFICATION OF RELATED HLAS POTENTIALLY ASSOCIATED WITH LONG-TERM NON-PROGRESSION
2bvo: STRUCTURES OF THREE HIV-1 HLA-B5703-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES AND IDENTIFICATION OF RELATED HLAS POTENTIALLY ASSOCIATED WITH LONG-TERM NON-PROGRESSION -
 2bvp: STRUCTURES OF THREE HIV-1 HLA-B5703-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES AND IDENTIFICATION OF RELATED HLAS POTENTIALLY ASSOCIATED WITH LONG-TERM NON-PROGRESSION
2bvp: STRUCTURES OF THREE HIV-1 HLA-B5703-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES AND IDENTIFICATION OF RELATED HLAS POTENTIALLY ASSOCIATED WITH LONG-TERM NON-PROGRESSION -
 2bvq: STRUCTURES OF THREE HIV-1 HLA-B5703-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES AND IDENTIFICATION OF RELATED HLAS POTENTIALLY ASSOCIATED WITH LONG-TERM NON-PROGRESSION
2bvq: STRUCTURES OF THREE HIV-1 HLA-B5703-PEPTIDE COMPLEXES AND IDENTIFICATION OF RELATED HLAS POTENTIALLY ASSOCIATED WITH LONG-TERM NON-PROGRESSION -
 2c7u: CONFLICTING SELECTIVE FORCES AFFECT CD8 T-CELL RECEPTOR CONTACT SITES IN AN HLA-A2 IMMUNODOMINANT HIV EPITOPE.
2c7u: CONFLICTING SELECTIVE FORCES AFFECT CD8 T-CELL RECEPTOR CONTACT SITES IN AN HLA-A2 IMMUNODOMINANT HIV EPITOPE. -
 2cii: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF H-2DB COMPLEXED WITH A PARTIAL PEPTIDE EPITOPE SUGGESTS AN MHC CLASS I ASSEMBLY-INTERMEDIATE
2cii: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF H-2DB COMPLEXED WITH A PARTIAL PEPTIDE EPITOPE SUGGESTS AN MHC CLASS I ASSEMBLY-INTERMEDIATE -
 2cik: INSIGHTS INTO CROSSREACTIVITY IN HUMAN ALLORECOGNITION: THE STRUCTURE OF HLA-B35011 PRESENTING AN EPITOPE DERIVED FROM CYTOCHROME P450.
2cik: INSIGHTS INTO CROSSREACTIVITY IN HUMAN ALLORECOGNITION: THE STRUCTURE OF HLA-B35011 PRESENTING AN EPITOPE DERIVED FROM CYTOCHROME P450. -
 2clr: THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF A PEPTIDE EXTENDING OUT ONE END OF A CLASS I MHC BINDING SITE
2clr: THREE DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF A PEPTIDE EXTENDING OUT ONE END OF A CLASS I MHC BINDING SITE -
 2d31: Crystal structure of disulfide-linked HLA-G dimer
2d31: Crystal structure of disulfide-linked HLA-G dimer -
 2d4d: The Crystal Structure of human beta2-microglobulin, L39W W60F W95F Mutant
2d4d: The Crystal Structure of human beta2-microglobulin, L39W W60F W95F Mutant -
 2d4f: The Crystal Structure of human beta2-microglobulin
2d4f: The Crystal Structure of human beta2-microglobulin -
 2dyp: Crystal Structure of LILRB2(LIR2/ILT4/CD85d) complexed with HLA-G
2dyp: Crystal Structure of LILRB2(LIR2/ILT4/CD85d) complexed with HLA-G -
 2esv: Structure of the HLA-E-VMAPRTLIL/KK50.4 TCR complex
2esv: Structure of the HLA-E-VMAPRTLIL/KK50.4 TCR complex -
 2f53: Directed Evolution of Human T-cell Receptor CDR2 residues by phage display dramatically enhances affinity for cognate peptide-MHC without apparent cross-reactivity
2f53: Directed Evolution of Human T-cell Receptor CDR2 residues by phage display dramatically enhances affinity for cognate peptide-MHC without apparent cross-reactivity -
 2f54: Directed evolution of human T cell receptor CDR2 residues by phage display dramatically enhances affinity for cognate peptide-MHC without increasing apparent cross-reactivity
2f54: Directed evolution of human T cell receptor CDR2 residues by phage display dramatically enhances affinity for cognate peptide-MHC without increasing apparent cross-reactivity -
 2f74: Murine MHC class I H-2Db in complex with human b2-microglobulin and LCMV-derived immunodminant peptide gp33
2f74: Murine MHC class I H-2Db in complex with human b2-microglobulin and LCMV-derived immunodminant peptide gp33 -
 2f8o: A Native to Amyloidogenic Transition Regulated by a Backbone Trigger
2f8o: A Native to Amyloidogenic Transition Regulated by a Backbone Trigger -
 2fyy: The role of T cell receptor alpha genes in directing human MHC restriction
2fyy: The role of T cell receptor alpha genes in directing human MHC restriction -
 2fz3: The role of T cell receptor alpha genes in directing human MHC restriction
2fz3: The role of T cell receptor alpha genes in directing human MHC restriction -
![2git: Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 in complex with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide](//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1f/PDB_2git_EBI.jpg/180px-PDB_2git_EBI.jpg) 2git: Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 in complex with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide
2git: Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 in complex with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide -
![2gj6: The complex between TCR A6 and human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide](//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0c/PDB_2gj6_EBI.jpg/180px-PDB_2gj6_EBI.jpg) 2gj6: The complex between TCR A6 and human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide
2gj6: The complex between TCR A6 and human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide -
 2h26: human CD1b in complex with endogenous phosphatidylcholine and spacer
2h26: human CD1b in complex with endogenous phosphatidylcholine and spacer -
 2h6p: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3501 presenting the human cytochrome P450 derived peptide, KPIVVLHGY
2h6p: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3501 presenting the human cytochrome P450 derived peptide, KPIVVLHGY -
 2hjk: Crystal Structure of HLA-B5703 and HIV-1 peptide
2hjk: Crystal Structure of HLA-B5703 and HIV-1 peptide -
 2hjl: Crystal Structure of HLA-B5703 and HIV-1 peptide
2hjl: Crystal Structure of HLA-B5703 and HIV-1 peptide -
 2hla: SPECIFICITY POCKETS FOR THE SIDE CHAINS OF PEPTIDE ANTIGENS IN HLA-AW68
2hla: SPECIFICITY POCKETS FOR THE SIDE CHAINS OF PEPTIDE ANTIGENS IN HLA-AW68 -
 2hn7: HLA-A*1101 in complex with HBV peptide homologue
2hn7: HLA-A*1101 in complex with HBV peptide homologue -
 2nw3: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3508 presenting EBV peptide EPLPQGQLTAY at 1.7A
2nw3: Crystal structure of HLA-B*3508 presenting EBV peptide EPLPQGQLTAY at 1.7A -
 2nx5: Crystal structure of ELS4 TCR bound to HLA-B*3508 presenting EBV peptide EPLPQGQLTAY at 1.7A
2nx5: Crystal structure of ELS4 TCR bound to HLA-B*3508 presenting EBV peptide EPLPQGQLTAY at 1.7A -
 3hla: HUMAN CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN A2.1
3hla: HUMAN CLASS I HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN A2.1
























































































































































![2git: Human Class I MHC HLA-A2 in complex with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1f/PDB_2git_EBI.jpg/180px-PDB_2git_EBI.jpg)
![2gj6: The complex between TCR A6 and human Class I MHC HLA-A2 with the modified HTLV-1 TAX (Y5K-4-[3-Indolyl]-butyric acid) peptide](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0c/PDB_2gj6_EBI.jpg/180px-PDB_2gj6_EBI.jpg)


















