Eldorado Mountain

Eldorado Springs, Colorado[3]
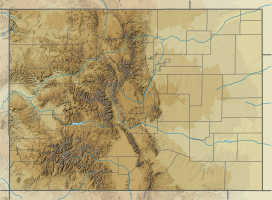
Eldorado Mountain is a mountain summit on the eastern flank of the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains of North America. The 8,344-foot (2,543 m) peak is located 8.1 miles (13.1 km) south by west (bearing 196°) of downtown Boulder, Colorado, United States.[1][2][3] The mountain is largely in Boulder County but it straddles the border and its southern flanks are located in Jefferson County. Its name was probably borrowed from the nearby community of Eldorado Springs.
Ownership
On the Boulder County side, about half of the mountain is owned by the City of Boulder; other large parcels are owned by Boulder County, Eldorado Canyon State Park and the Bureau of Land Management. On the Jefferson County side, various parcels are owned by private parties.
Dimensions
The lowest part of the mountain is its northeast toe with an elevation of about 5,800 feet (1,800 m)—giving the mountain a total height of about 2,500 feet (760 m). At its longest, the mountain measures about two miles (3 km) across on a south-east axis. The summit is owned by the City of Boulder. The City has a policy that restricts public access to this part of its holdings, and there is no trail going to the summit.[4]
Near the top of the mountain is a large antenna field with two buildings overlooking the steep slope on the east. The radio station KBCO transmits from this site. The site is reached by a private dirt road that starts further south in Plainview (a small community with less than a dozen homes) and then climbs the steep southern flanks.
East side
On the east flank of Eldorado Mountain is its largest cliff, Mickey Mouse Wall. When viewed from the north, two buttresses at the top of the cliff look like a pair of mouse ears. But, from the east, Mickey Mouse looks just like one of the flatirons. The only trail on this side of the mountain is a climber's trail accessing Mickey Mouse Wall. (As of September 2007, the City of Boulder was planning to re-align this trail.) Also on the east flank are the remains of the Conda Quarry, covering about 7 acres (28,000 m2). The quarry operated from the 1950s through the 1980s. In 1992, in order to preserve the land as open space, the City of Boulder purchased the quarry along with the underlying land and mining rights. Later, the City undertook a reclamation project on the site,[5] although the quarry is still visible. Down from the quarry on the access road is the Eldorado Mountain Yoga Ashram.
South side
To the immediate south of the mountain is Bull Gulch, which becomes the Doudy Draw, first heading eastward but then turning northward and joining South Boulder Creek.
West side
From the saddle between Eldorado Mountain and Crescent Mountain an abandoned road descends to the railroad tracks. To the west of the mountain is South Draw, a small basin that drains into South Boulder Creek.
North side
To the north of the mountain is South Boulder Creek, a large creek that starts near the Continental Divide, passes through Gross Reservoir and later joins Boulder Creek about six miles (10 km) downstream. Located along this creek is Eldorado Canyon State Park. Within the Park is the Rattlesnake Gulch Trail that climbs about halfway up the north flank of Eldorado Mountain. Near the top of this trail is the site of the former Crags Hotel, which was in business from 1908 until 1913 when it burned down. The Park has converted the hotel ruins into a historic site for visitors. When it was operating, the hotel also ran a funicular that went down from the hotel to the creek. Still on the north side are three thin cliffs bands lined in a single column—Continental Crag, Upper Peanuts Wall, and Lower Peanuts Wall—from top to bottom. At the very base of the flank is the famous tower-like Bastille. Further down the creek is the unincorporated community of Eldorado Springs.
Railroads and aqueducts
On the northern flanks of the mountain are four different lines: two railroad grades and two aqueducts. The top-most line (located at about the 7,100-foot (2,200 m) level) is a railroad line owned and operated by Union Pacific Railroad. It circles three quarters of the mountain, passing through a dozen tunnels along the way. Construction began in 1902 and was known at the time as Moffat Road. About twenty miles (32 km) to the west, this line continues through the Moffat Tunnel under the Continental Divide. Amtrak’s California Zephyr runs along this line every day, once each way.
Another line (located at about the 6,300-foot (1,900 m) level) is the aqueduct known as the South Boulder Diversion. It leads to Ralston Reservoir, supplying water to Denver and some of its surrounding suburbs. It was built in 1937 and is owned by Denver Water, a governmental agency whose commissioners are appointed by the mayor of Denver.[6] Near Eldorado Mountain, the aqueduct is mostly hidden in tunnels, but in three short sections it emerges above ground as a large pipeline. Further east, it becomes a canal.
A third line (located at about the 6,100-foot (1,900 m) level) is another railroad grade. Known as the Denver Utah & Pacific, it was originally graded in the 1880s. No tracks were ever laid, and for that reason historians refer to it as a “ghost” railroad. After being abandoned by the railroad, the grade was used by the public as an access route to the west side of the canyon. The grade continued to be the only such access until 1927 when the present road at the bottom of the canyon was built. In 1978, part of the grade became part of the newly created Eldorado Canyon State Park and was later converted into the Fowler Trail.
The bottom line is the Community Ditch (located at about the 5,800-foot (1,800 m) level). It begins at a diversion dam located at the northeast toe of Eldorado Mountain (also being the location of the entrance to Eldorado Canyon State Park.) The ditch drains into Marshall Lake three miles (5 km) to the east. It was built around 1908 and is owned by Farmers Reservoir and Irrigation Company.
Gallery
-
 Northeast toe, lowest point
Northeast toe, lowest point -
 NNE view
NNE view -
 The Conda Quarry
The Conda Quarry -
 ENE view
ENE view -
 The Mouse Ears
The Mouse Ears -
 Antenna field near the top
Antenna field near the top -
 Union Pacific train, with Mickey Mouse Wall
Union Pacific train, with Mickey Mouse Wall - Bull Gulch
-
 SE view
SE view -
 SSE view
SSE view -
 SW view
SW view -
 WSW view
WSW view -
 NW view
NW view -
 NNW view
NNW view -
 South Draw
South Draw -
 Rattlesnake Gulch
Rattlesnake Gulch -
 Continental and Peanuts
Continental and Peanuts - The Bastille
-
 Portion of USGS Topo Map
Portion of USGS Topo Map
See also
- List of Colorado mountain ranges
- List of Colorado mountain summits
- List of Colorado county high points
Footnotes
- ^ a b The elevation of Eldorado Mountain includes an adjustment of +1.202 m (+3.94 ft) from NGVD 29 to NAVD 88.
- ^ a b c d e "Eldorado Mountain, Colorado". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved November 5, 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Eldorado Mountain". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved November 5, 2014.
- ^ Visitor Master Plan adopted by Boulder City Council on April 12, 2005
- ^ Boulder Daily Camera, June 24, 1996
- ^ Article X of the Charter of the City and County of Denver
References
- Topographical Map USGS Eldorado Springs
- Sampson, J., High, Wild and Handsome (2000)
- Rossiter, R. Rock Climbing Eldorado Canyon (2000)
External links
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons News from Wikinews
News from Wikinews Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Texts from Wikisource
Texts from Wikisource Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks Resources from Wikiversity
Resources from Wikiversity
- People for Eldorado Mountain An advocacy group, conservation-oriented.
- City of Boulder's Open Space and Mountain Parks Department with responsibility for city lands on Eldorado Mountain.
- Denver Water
- Eldorado Mountain Yoga Ashram
- Mountain Project Climbing website. Look under Colorado → Boulder → Eldorado Mountain and Eldorado Canyon SP.
- Denver Public Library for old photos. Search "Crags Hotel"; "Eldorado Community" for Community Ditch.
- v
- t
- e
- Mount Garfield
- Aspen Mountain
- Capitol Peak
- Castle Peak
- Cathedral Peak
- Chair Mountain
- Crested Butte
- Gothic Mountain
- Italian Mountain
- Maroon Bells
- Mount Emmons
- Mount Owen
- Mount Sopris
- Pyramid Peak
- Snowmass Mountain
- Snowmass Peak
- Treasure Mountain
- Black Mountain (Moffat County)
- Columbus Mountain
- Elk Mountain (Routt County)
- Hahns Peak
- Flat Top Mountain
- Sleepy Cat Peak
- Eagles Nest
- Jacque Peak
- Meridian Peak
- Mount Powell
- The Spider
- Crater Peak
- North Mamm Peak
- Clark Peak
- Arkansas Hills
- Clinton Peak
- Dyer Mountain
- Gemini Peak
- Horseshoe Mountain
- Mount Arkansas
- Mount Bross
- Mount Buckskin
- Mount Democrat
- Mount Lincoln
- Mount Sheridan
- Mount Sherman
- Pacific Peak
- West Buffalo Peak
- Elk Mountain (Grand County)
- Parkview Mountain
- Radial Mountain
- Whiteley Peak
| Sangre de Cristo Range |
|
|---|---|
| Wet Mountains |
|
| Others |
|
| Collegiate Peaks |
|
|---|---|
| Others |
|
- Crystal Peak
- Fletcher Mountain
- Peak 10
- Peak One
- Quandary Peak
- Tenmile Peak
- Bear Mountain
- Blair Mountain
- Chalk Mountains
- Cochetopa Hills
- Dawson Butte
- Diamond Peak
- Flirtation Peak
- Granite Peak
- Grand Hogback
- Grannys Nipple
- Horsefly Peak
- Lead Mountain (Grand County)
- Mount Neva
- Powell Peak
- San Luis Hills
- Storm King Mountain
- Terrible Mountain
- Two Buttes
- Ute Mountain