| SCYL2 |
|---|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | SCYL2, CVAK104, SCY1 like pseudokinase 2, AMCNACC, AMC4 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 616365; MGI: 1289172; HomoloGene: 13349; GeneCards: SCYL2; OMA:SCYL2 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 12 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 12q23.1 | Start | 100,267,140 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 100,341,715 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 10 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 10 C2|10 45.05 cM | Start | 89,474,583 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 89,522,147 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - mucosa of sigmoid colon
- corpus epididymis
- secondary oocyte
- jejunal mucosa
- palpebral conjunctiva
- amniotic fluid
- oral cavity
- rectum
- tail of epididymis
- monocyte
|
| | Top expressed in | - secondary oocyte
- zygote
- hand
- primary oocyte
- lumbar spinal ganglion
- tail of embryo
- superior cervical ganglion
- granulocyte
- genital tubercle
- endocardial cushion
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 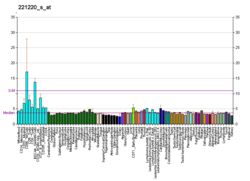 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - ATP binding
- signaling receptor binding
- protein kinase activity
- protein binding
| | Cellular component | - Golgi apparatus
- endosome membrane
- membrane
- cytoplasmic vesicle
- clathrin-coated vesicle
- cytoplasm
- endosome
- perinuclear region of cytoplasm
| | Biological process | - receptor internalization involved in canonical Wnt signaling pathway
- negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway
- protein phosphorylation
- endosome to lysosome transport
- positive regulation of clathrin-dependent endocytosis
- positive regulation of receptor internalization
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_017988
NM_001317784
NM_001330253
NM_001330254
NM_001330256 |
| |
|---|
NM_198021
NM_001310704
NM_001358843 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | |
|---|
NP_001304713
NP_001317182
NP_001317183
NP_001317185
NP_060458 |
| |
|---|
NP_001297633
NP_932138
NP_001345772 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 12: 100.27 – 100.34 Mb | Chr 10: 89.47 – 89.52 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|


















